Nutritional and Functional Properties of Moringa Leaves − From Germplasm, to Plant, to Food, to Health
Ray-Yu Yang, Lien-Chung Chang, Jenn-Chung Hsu, Brian B. C. Weng Manuel,
C. Palada , M. L. Chadha, and Virginie Levasseur
Nutrition, Plant Breeding, and 5 Crop and Ecosystem Management, AVRDC− The World Vegetable
Center, PO Box 42, Shanhua, Tainan, Taiwan, ROC.
Animal Science Department, National Chung-Hsin University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC Applied Microbiology, National Chiayi University, Chiayi, Taiwan, ROC AVRDC Regional Center for Africa, PO Box 10, Duluti, Arusha, Tanzania AVRDC West Africa Office, BP 320, Bamako, Mali
Summary
Increased vegetable utilization and consumption are critical to alleviate world-wide incidence of nutritional deficiencies. Diets rich in micronutrients and antioxidants are strongly recommended to ameliorate the effects of HIV/AIDS. Our survey of over 120 species of tropical and subtropical edible plants for nutrient content, antioxidant activity (AOA), and crop traits indicated that Moringa oleifera is one of the promising crops which could contribute to increased intake of micronutrients and antioxidants. Moringa have been included in the AVRDC Nutrition Seed Kit. Each kit includes different kinds of vegetable seeds for planting in home gardens to ensure good health and nutrition of household recipients. The Nutrition Kit is promoted and distributed by the AVRDC Regional Center for Africa to farmers, women groups, and extension people.
Genetic variation, environmental factors, postharvest handling and different means of food preparation influence the nutritional and functional qualities of moringa. The highest nutrient values among four moringa species evaluated were measured on M. oleifera. AVRDC designed methods for high density planting and pruning enabled convenient and continuous harvests of young shoots for fresh market. We found that harvest season and leaf stage significantly influenced nutrient contents of moringa leaves. Higher protein, vitamin A and glucosinolates contents and AOA were obtained in hot-wet season; whereas, higher iron, vitamin C, and phenolic contents were found in cool-dry season. Variation among 10 M. oleifera accessions for nutrient contents were small and thus varietal selection should focus on horticulture traits. Mature leaves were more nutritious than young shoots and could be quickly dried with minimum nutrient loss; however, young shoots exhibited better eating quality and thus were better accepted for fresh market. Cooking increased availability of iron and enhanced aqueous AOA. The AOA was maintained after simulated digestion.
Moringa leaf extracts exhibited anti-microbial activity including inhibition of the growth of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from food and animal intestines. Moringa added to fodder could be a potential bioceutical agent to substitute for antibiotics in livestock production. For human use, intervention with a diet containing 5% moringa powder was investigated using a rat model and compared to a 5% common cabbage diet, and a nutrient-sufficient diet without vegetable. The study implies the consumption of moringa enhances the immune response of nutrient Moringa and other highly nutritious plant resources: Strategies, standards and markets for a better impact on nutrition in Africa. Accra, Ghana, November 16-18, 2006 2 sufficient subjects. In addition, consumption of nutrient and phytochemical-rich vegetables, like moringa, leads to a better immune response compared to consumption of vegetables that are rich in fiber but lower in nutrient content, like common cabbage. Moringa should be promoted for greater consumption to improve nutrition and strengthen immune functions for fighting infectious diseases.
Introduction
Iron and vitamin A deficiencies, and infectious diseases continue to devastate people of the developing world; non-communicable diseases attributable to obesity are increasingly common in developed and developing countries. Diets rich in vegetables and fruits providing micronutrients and health-promoting phytochemicals could alleviate both under-nutrition and obesity.
Most people in the world lack adequate access to vegetables even though they are essential for good health. Insufficient vegetable and fruit consumption causes 2.7 million deaths annually worldwide and belongs to the top 10 risk factors contributing to mortality (Ezzati et al., 2002). Malnutrition is rampant in the tropics where per capita vegetable supplies in most countries falls far short of the minimum recommended 73 kg/person/year. In Sub-Saharan Africa, per capita vegetable supplies are only 43% of what are needed, leading to widespread malnutrition.
There are hundreds o.f plant species consumed as vegetables, but only about 20 crops are produced in intensive cropping systems (Siemonsma and Piluek, 1994). Indigenous vegetables (IVs) are native to a particular region or introduced to the region from another geographical area over a long period of time. They are grown locally in a small scale, often resistant to diseases and tolerant to environmental stresses, very nutritious and contain a vast range of phytochemicals; however, most are neglected or under-utilized. IVs have potential for introduction or greater use as cash crops in peri-urban systems, vegetables for daily sustenance in home gardens, and a means to diversify production systems and diets.
Nutrient contents of vegetables vary greatly. Among 240 edible plants of 120 species tested at the AVRDC, β-carotene content were measured and ranged 0 − 22 mg with the average of 3.1 ± 3.3 mg based on 100 g fresh weight (fw) basis. Iron content ranged 0.2 − 26 mg/100g fw and averaged 2.1 ± 2.6 mg/100g fw. Vegetable sample distributions for β-carotene and iron contents were screwed with the majority of samples ≤ 4 mg/100g for β-carotene and ≤ 2 mg/100g for iron. With the survey of 120 edible plant species, Moringa oleifera were found among the most promising species according to their high antioxidant activity, high contents of micronutrients and phytochemicals, processing properties, ease of growing and palatability. In this paper, we present nutritional and bioactive values of moringa leaves from germplasm, to field, to plate and to health outcome.
Nutrient and phytochemical contents among four Moringa species
We compared antioxidant and nutritional values of four Moringa species (Yang et al., 2006). M. stenopetala is the most economically important species after M. oleifera among Moringas; M. drouhardii has the most pungent odor similar to mustard oil; and M. peregrine has the widest habitat range and the only one of the slender trees extended out of Asia (Olson, 2001).
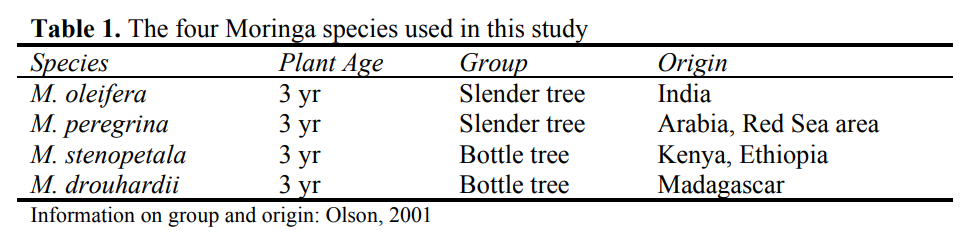
Nutritional Quality of the Four Species
Among the four species, M. oleifera contained the highest amounts of β-carotene, ascorbate (Vit C), α-tocopherol (Vit E) and iron, and was the second highest in protein content (Table 2). M. oleifera grows faster than the other three species under the subtropical low lands in Taiwan, and this specie is commonly consumed as a vegetable in South Asia and Africa. Oligosaccharides and oxalate were reported as anti-nutrient factors in Moringa leaves (Freiberger et al., 1998). In this study, stachyose and raffinose were not found in mature leaves, but detected in young leaves (0− 14 mg/g dry weight) and in seeds (22−98 mg/g dw). Moringa mature leaves contained very low value of oxalate (0.99 ± 0.21 mg/g dw) by compared to spinach (25−45 mg/g dw). The data indicated that oxalate and oligosaccharides are not
significant anti-nutrient factors in Moringa.
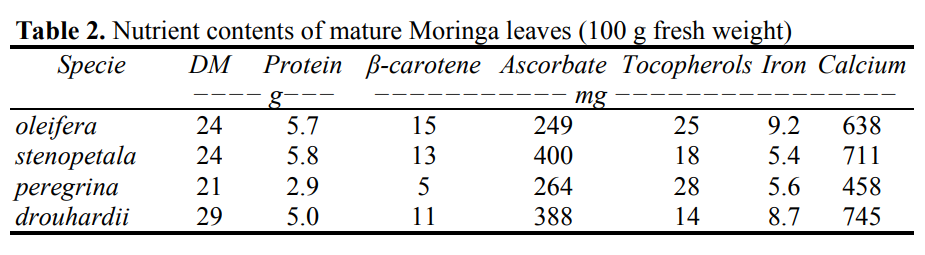
Antioxidant Contents of Moringa
Concentrations of four natural antioxidants (total phenolics and antioxidant vitamins A, C and E) were measured for the four species. The content ranges on a dry weight basis were 74−210 µmol/g for phenolics, 70−100 µmol/g for ascorbate (Vit C), 1.1−2.8 µmol/g for β-carotene and 0.7 − 1.1 µmol/g for α-tocopherol (Vit E) (Figure 1). Antioxidant content of Moringas are high even compared to vegetables and fruits known for high antioxidant contents such as strawberries high in phenolics (330 mg gallic acid (GA)/100g fw, or ~190 µmol GA/g dw); hot pepper high in ascorbate (200 mg/100g fw, or ~110 µmol/g dw), carrot high in β-carotene (10 mg/100g fw, or ~1.8 µmol/g dw) and soybean which is high in α-tocopherol (0.85 mg/100g fw, or ~1.8 µmol/g dw). Moringas are an excellent source of a wide spectrum of dietary antioxidants.
In summary: (1) high nutrients, antioxidants and glucosinolates, and low oxalate contents are common features of the four M. pecies; and (2) M. peregrina was the uppermost for antioxidant; M. oleifera has the highest nutrient values among the four
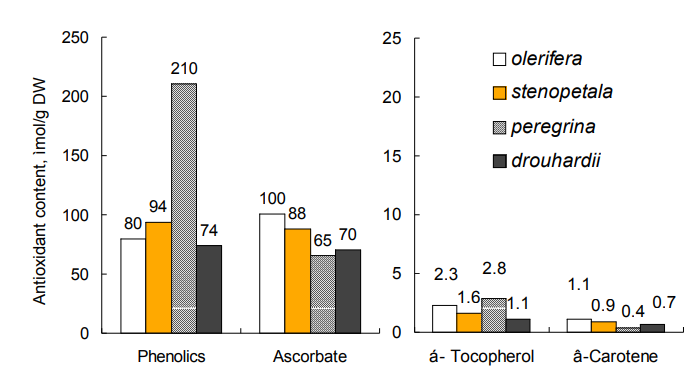
Figure 1. Antioxidant contents of the four Moringa species
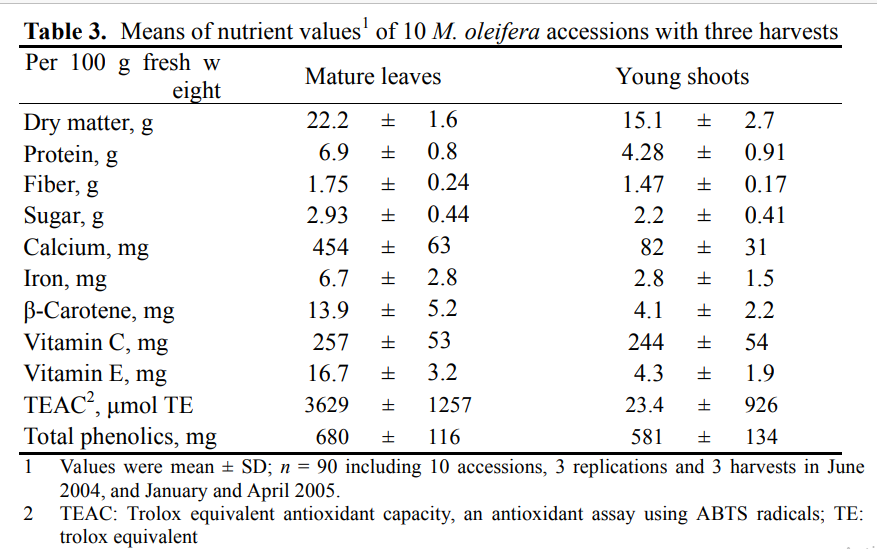
Nutrient and phytochemical contents in Moringa leaves as affected by different accessions, harvesting seasons and leaf stages
Ten M. oleifera accessions, selected from a survey of 60 M. oleifera accessions for yield and growth performance, were used in the study. The seeds, collected from Taiwan, Phillipines, India, USA and Tanzania, were sown on 30 March 2004, and transplanted to the field on 26 April 2004. Plants were grown on 6-m-long x 1.5-m-wide x 30-cm-high raised beds, in double rows with 30 cm between rows and plants within rows. Accessions were arranged in a RCBD with 40 plants per plot and 3 replications. No pesticide was applied. Plots were harvested for young shoots 1-2 times per week from three harvest periods: 30 June − 7 December 2004, 24 Jan − 30 March 2005, and 25 April − 15 December 2005 with about one month interval of each harvesting period to allow mature leaves growth. The average air temperatures and rain falls were 29.2°C (23.9 − 34.6°C) and 13.9 mm in June 2004 as hot-wet season, 17.7°C (6.7−27.4°C) and 0.1 mm in January 2005 as cool-dry season, and 24.7°C (15.4−32.8°C) and 1.1 mm in April 2005. Young shoots and mature leaves were collected separately from the branches harvested the first day of the three harvest periods and sent to laboratory. Nutrient contents and antioxidants were measured. The averaged values are shown in Table 3.
This study indicated that: (1) High density planting and frequently trimming enable convenient and continuous weekly harvests of young shoots (Figure 2). (2) Variation among 10 M. oleifera accessions for nutrient contents was small (data not shown) so breeding for higher nutrient content is not worthwhile. Varietal selection should focus on horticultural traits. (3) Mature leaves were more nutritious than young shoots and could be quickly dried with minimum nutrient loss; however, young shoots exhibited better eating quality and more acceptable for the fresh market. (4) Seasonal effects caused 1.5–3 times content variation for vitamin A, iron and antioxidants in moringa leaves; higher vitamin A was obtained in hot-wet season while higher iron and vitamin C were found in cool-dry.

Nutrient and phytochemical contents in Moringa leaves as affected by processing temperature and simulated gastrointestinal digestion
Leafy vegetables are often cooked before consumption and dried in preservation during time of scarcity of vegetables. Sun-drying in direct sunshine and under shade are the common practices used in most parts of Africa to preserve vegetables for dry season consumption (Lyimo et al., 1991). However ways of food preparation and preservation may affect significantly the concentration and availability of minerals, vitamins and other essential compounds in food. Some reports have documented the losses of nutrients from vegetables during drying (Yadav and Sehgal, 1997) and cooking (Kachik et al., 1992 and Kidmose et al., 2005). A low temperature oven drying process was applied to dehydrate moringa leaves. The nutrient values were measured and compared to those of freeze dried leaves (Figure 3). The results sowed that drying at 50°C for 16 hours maintained most nutrients and phytochemicals in moringa leaves except for vitamin C. The mild-heating and drying process could be achieved using common household facility such as stove to provide a simple and effective way for long term preservation and continuous supply of essential micronutrients.
Our previous study on in vitro iron bioavailability (IB) of vegetables indicated that cooking increases IB of certain vegetables 2−10 times (Yang et al., 2002). The cooking enhancing effect can be achieved with different heating processes including boiling, stir-frying and hot-air drying. Prolonged storage of cooked vegetables will reduce the availability of iron. In the case of cabbage, the cooking enhancing effect was due to the reduction of iron-polyphenol interaction, which commonly occurs during plant cell destruction. The nature of the enhancing factors in these vegetables was similar to the effect of EDTA, which stabilizes iron when it is released from cell (Yang and Tsou, 2006). In he case of Moringa, boiling in water enhanced the in vitro IB of fresh leaves and dried powder by 3.5 and 3 times, respectively (Figure 4). Cooking Moringa leaves also raised total available iron of mixtures with other food items such as mungbean (Yang et al., 2006). In addition, boiling Moringa leaves in water enhanced aqueous AOA, and the AOA was maintained after simulated digestion.
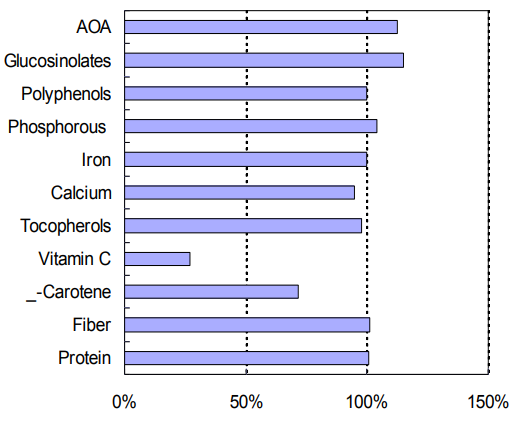
Concentration ratio (oven dry /freeze dry)
Figure 3. Ratio of nutrient and phytochemical content of oven dried leaves to freeze dried leaves. AOA: antioxidant activity; TG total glucosinolates
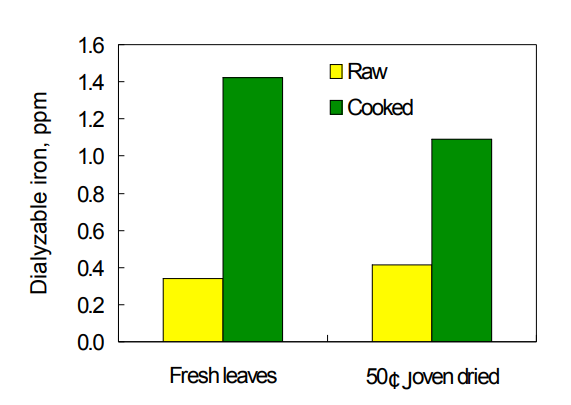
Figure 4. In vitro iron bioavailability of Moringa leaves, raw and cooked
Immune modulation of dried Moringa powder in diets for human use and livestock production
Intervention with a diet containing 5% moringa powder was investigated using a rat model and compared to a 5% common cabbage diet, and a nutrient-sufficient diet without vegetable. After 3 weeks, the preliminary result (data not shown) indicated that the moringa diet lightly reduced blood triglycerides and enhanced immune response due to increased peripheral and splenocyte T-cell proliferations. The preliminary study implies the consumption of moringa may increase immune response of nutrient-sufficient subjects. In addition, consumption of nutrient and phytochemical-rich vegetables, like moringa, leads to a better immune response compared to consumption of vegetables that are rich in fiber but lower in nutrient or phytochemical content, like common cabbage. Moringa should be promoted for greater consumption for human use to improve nutrition and strengthen immune functions.
The effects of dehydrated leaves of M. oleifera in the diets of broilers were also investigated. The trial included 5 treatments (diet without moringa and diets containing 0.5%, 1%, 2% and 3% dried leaves) with 3 replications and 4 broilers per replication. Twenty-one day old broilers were housed in wire cages for one week adaptation followed by a 3-week-experimental feeding period. Feed and water were supplied ad libitum. Growth performance, immune function and ileum microflora were evaluated. The results (data not shown) indicated that Moringa diets significantly (1) enhanced duodenum traits; (2) increased concentrations of total globulin, γ-globulin and IgA, lymphocyte ratio, antibody titer to sheep erythrocytes, and delayed type hypersensitivity (3) reduced E. coli and increased Lactobacillus counts in ileum. In conclusion: Moringa oleifera leaves are potential plant material to enhance immune responses and improve intestinal health of broilers. The efficacy of Moringa oleifera as bioceutical agents to substitute for antibiotic use for broiler production will be further examined
Promotion of Moringa for greater production and consumption
High nutrients, antioxidants and glucosinolates are common features of Moringa species. However, leaf stages and harvesting seasons can change their nutritional values 1.5 − 3 times, especially for β-carotene and iron. Variation among M. oleifera accessions for nutrient contents were small, varietal selection should focus on horticulture traits. Cooked moringa leaves provide more bio-available iron. Mild-heat drying process (50 °C/ 16 hours) maintained most nutrients and bioactives in moringa leaves and could be achieved by low-cost household preparation as a simple and effective way for continuous nutrients/bioactives supply. The dried leaves provide many kinds and types of nutrients and bioactives, which would lead to better nutrition and health.
AVRDC Regional Center in Africa includes Moringa seeds with other African indigenous vegetable seeds such as amaranth, nightshades, cowpea, okra, African eggplant, crotolaria, corchorus in Nutrition Seed Kit for gardening. The seed kits are distributed to researchers, agriculture/ nutrition extension workers for farmers’ training and school children education, and given to individual farmers to grow vegetables in home gardens to ensure good health and nutrition of household recipients.
Reference
Ezzati, F., Lopez, A.D., Rodgers, A., Hoorn, S.V. and Murray, C.J.L. 2002. Selected ajor risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet 360 (9343): 1347-1360.
Freiberger, C. E.; Vanderjagt, D. J.; Pastuszyn, A.; Glew, R. S.; Mounkaila, G.; Millson, M.; Glew, R. H. 1998. Nutrient content of the edible leaves of seven wild plants from Niger. Plant Foods for Hum. Nutr. 53: 57 – 69.
Kachik, F., Mudlagiri, B.G., Gary, R.B, Joanne, H., Lusby, W.R., Maria, D.T. and arrera, M.R. (1992). Effects of food preparation on qualitative and quantitative distribution of major carotenoids constituents of tomatoes and several green vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 40, 390-398.
Kidmose, U., Yang, R. Y., Thilsted, S. H., Christensen, L. P. and Brandt, K. 2006. Content of carotenoids in commonly consumed Asian vegetables and stability and extractability during frying. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis.19: 562−571.
Lyimo, M., Nyagwegwe, S, and Mukeni, E. 1991. Investigation of the traditional food processing, preservation and storage methods on vegetable nutrients; a case study of Tanzania, Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 41:53-57.
Olson, M. E. 2001. Introduction to the Moringa family. p11−28. In: L. L. Fuglie (ed.), The Miracle Tree − Moringa oleifera: Natural Nutrition for the Tropics. Church World Service, West Africa Regional Office, Dakar, Senegal.
Siemonsma, J.S. and Piluek, K. (eds). 1994. Vegetables. Bogor: Plant Resources of South-East Asia.
Yadav, S.K and Sehgal, A. 1997. Effect of home processing on ascorbic acid and beta carotene content of bathua (Chenopodium album) and fenugreek (Trigonella foenungraecum) leaves. Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 50: 239-247.
Yang, R.Y., Tsou, S. C. S. and Lee, T. C. 2002. Effect of cooking on in vitro iron bioavailability of various vegetables. p130-142. In: T.C. Lee and C.T. Ho (eds.), Bioactive Compounds in Foods: effect of processing and storage. American Chemical Society, Washington, D. C.
Yang, R. Y. and Tsou, S. C. S. 2006. Enhancing iron bioavailability of vegetables through proper preparation − principles and applications. Journal of International Cooperation. 1: 107−119.
Yang, R.Y., Tsou, S. C. S., Lee, T. C., Chang, L. C., Kuo, G., and Lai, P. Y. 2006. Moringa, a novel plant rich in antioxidants, bioavailable iron, and nutrients. pp224-239. In: C. T. Ho (ed) Challenges in Chemistry and Biology of Herbs. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.
Credit : Moringa and other highly nutritious plant resources: Strategies, standards and markets for a better impact on nutrition in Africa. Accra, Ghana, November 16-18, 2006